
UK Passport Renewals. Made Easy.
UK Passport
Renewal

Welcome to passportrenewal.org.uk!
Explore our web site and if you have any questions, please drop us an email.
Online resource for UK passport renewals | Give you a helping hand
UK Passport Offices



Popular Pages
Passport Renewal Scams
Passport Renewal Fees
24 hour Passport Renewal



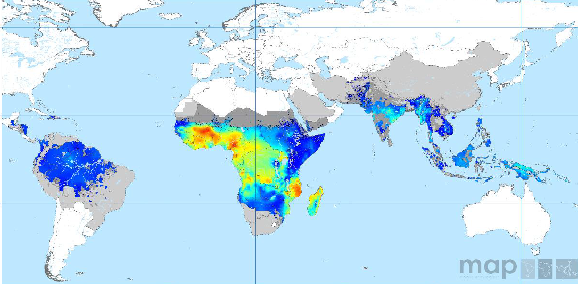
Symptoms of Malaria
Whilst travelling it is important to be aware of the health risk of malaria. Malaria is a serious fever like illness transmitted by mosquitoes. Malaria attacks the red blood cells with a parasite called Plasmodium.
The symptoms of malaria can be confusing as they are similar common symptoms and signs of other illness. Malaria symptoms sometimes causes misdiagnosis as influenza or viral hepatitis or gastroenteritis or lower respiratory tract infection.
Common symptoms of malaria
The symptoms of malaria can be confusing as they are similar common symptoms and signs of other illness. Malaria symptoms sometimes causes misdiagnosis as influenza or viral hepatitis or gastroenteritis or lower respiratory tract infection.
Common symptoms of malaria
|
●
|
Fever/sweats/chills
|
|
●
|
Feeling tired
|
|
●
|
Muscle pain, tenderness)
|
|
●
|
Headache
|
|
●
|
Diarrhoea
|
|
●
|
Cough
|
Symptoms of severe or complicated malaria in adults
|
●
|
Impaired consciousness or seizures
|
|
●
|
Renal impairment
|
|
●
|
Acidosis
|
|
●
|
Hypoglycaemia
|
|
●
|
Pulmonary oedema or acute respiratory distress syndrome
|
|
●
|
Haemoglobin
|
|
●
|
Spontaneous bleeding/disseminated intravascular coagulation
|
|
●
|
Shock (algid malaria)
|
|
●
|
Haemoglobinuria
|
Symptoms of severe or complicated malaria in children
|
●
|
Impaired consciousness or seizures
|
|
●
|
Respiratory distress or acidosis
|
|
●
|
Hypoglycaemia
|
|
●
|
Severe anaemia
|
|
●
|
Prostration (inability to sit or stand)
|
|
●
|
Parasitaemia
|
How to avoid getting malaria
Follow the ABCD of malaria prevention:
|
●
|
Awareness of the risk;
|
|
●
|
Bite prevention;
|
|
●
|
Chemoprophylaxis (preventive medication)
|
|
●
|
Diagnosis.
|
Awareness of the risk
Check your destination to see if malaria is a risk and visit your GP for travel health advice before you go.
Bite prevention
How to prevent being bitten by mosquitos
|
●
|
Use an insect repellent containing DEET (N,N-diethylmetatoluamide),
|
|
●
|
wear cover up clothing especially at night when mosquitoes are most active,
|
|
●
|
sleep under a bed net or in an air-conditioned room.
|
|
●
|
Mosquitoes require water in which to breed, so remove all sources of standing water
|
Chemoprophylaxis (preventive medication)
|
●
|
There are a number of different types of preventative medication, visit your doctor ideally 6 to 8 weeks before you travel.
|
|
●
|
You will be prescribed malaria tablets, make sure you take them as directed. Remember - to completed the full course of tablets when you get back to make sure you are properly protected.
|
|
●
|
Homoeopathic or herbal remedies do not protect against malaria and must not be used in place of antimalarial tablets.
|
Diagnosis
Unfortunately the above malaria prevention methods are not 100% effective. If after visit a high risk country you have any of these symptoms;
|
●
|
Fever/sweats/chills
|
|
●
|
Feeling tired
|
|
●
|
Muscle pain, tenderness)
|
|
●
|
Headache
|
|
●
|
Diarrhoea
|
If you have of the above make sure you visit your doctor urgently and inform them where you have been. Remember you could still get malaria, even a year after a trip to a high risk malaria area.
Is malaria infectious
If you get malaria and become ill, you cannot pass the infection on to anyone else. Malaria cannot be passed directly from person to person.